What is Hodgkin lymphoma?
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a cancer that starts in lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell. They are found in the bone marrow, blood and lymphatic system. They help protect the body against germs and abnormal cells, including cancer cells.
Classic Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) starts in abnormal B cells called Hodgkin and
Reed-Sternberg (HRS) cells. HRS cells are a lot bigger than normal B cells and have
1 or more large
Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (NLPHL) also starts in abnormal B cells, but they are different from HRS cells. The abnormal B cells in NLPHL are called lymphocyte-predominant (LP) cells. LP cells are sometimes called popcorn cells because they look large and puffy when viewed under a microscope. NLPHL is a very rare type of HL.
Another type of cancer that can start in lymphocytes is called non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL). The abnormal B cells of Hodgkin lymphoma look and behave differently from non-Hodgkin lymphoma cells. Hodgkin lymphomas and non-Hodgkin lymphomas are treated differently.
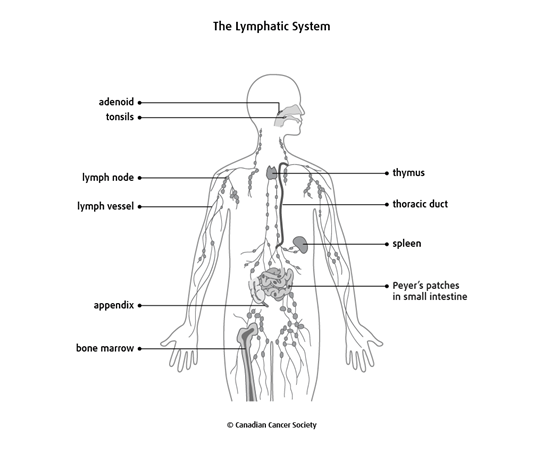
Hodgkin lymphoma starts in the
Types of Hodgkin lymphoma
Your trusted source for accurate cancer information
With support from readers like you, we can continue to provide the highest quality cancer information for over 100 types of cancer.
We’re here to ensure easy access to accurate cancer information for you and the millions of people who visit this website every year. But we can’t do it alone.
Every donation helps fund reliable cancer information, compassionate support services and the most promising research. Please give today because every contribution counts. Thank you.
