The human body
Our bodies are made up of trillions of cells that form tissues and organs. The body has about 200 different types of cells that do different jobs. Cells of the same type are grouped together to make tissues, like the lining of the intestine or the surface of the skin. And different types of tissues make up organs, like the lungs or liver.
Cells
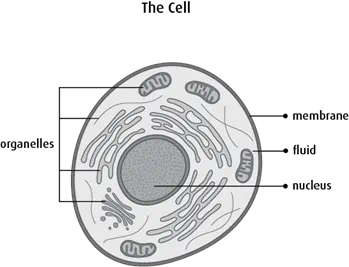
Cells are so small that they can only be seen with a microscope. Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things and they do all the main jobs to keep us alive. But no matter what their job is, all cells have the same basic parts. A membrane holds a cell together and controls what goes in and out of the cell. The inside of a cell is called the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm has many small parts called organelles, which are surrounded by fluid.
The nucleus is the largest and an important organelle inside the cell. It tells
a cell what to do and contains all our body’s genetic material (
Tissues
Tissues are made up of cells and extracellular matrix. Cells in a type of tissue are similar to each other and have similar jobs, like exchanging air in the lungs or absorbing nutrients in the intestine. Extracellular matrix is the material that fills the space in the tissue between cells. It strengthens, supports and protects tissue. When cancer develops, there is a loss of organization in a tissue. This means that the cells change and become abnormal and the extracellular matrix gets broken down as a cancer develops and grows.
Our bodies have 4 main types of tissue – epithelial, connective, muscle and neural.
Epithelial tissue
Epithelial tissue is made up of sheets of epithelial cells called
Connective tissue
Connective tissue holds parts of the body together and supports other tissues. It also protects the organs. Bone, cartilage, ligaments, tendons and fat are all connective tissues. Blood and lymph are also connective tissues. They are connective tissue in a liquid form, made up of cells in a fluid.
Epithelial tissue and connective tissue together can form membranes like the
Muscle tissue
The job of muscle tissue is to contract and relax. There are 3 types of muscle in the body.
Skeletal muscle makes up the muscles we can control, like the biceps in our arms or the quadriceps and hamstrings in our legs.
Smooth muscle makes up the muscles that we can’t control, like those in the organs of the digestive system that move food and waste through the body.
Cardiac muscle helps to circulate blood and maintain blood pressure. It is found only in the heart.
Neural tissue
Neural tissue sends electrical signals from one part of the body to another. These signals are mainly involved in sensation and movement. Neural tissue makes up the brain, spinal cord and nerves. There are 2 main cell types in neural tissue. Neurons are cells that send electrical signals, and neuroglia are cells that support neural tissue and provide nutrients to neurons.
Organs and organ systems
An organ, such as the kidney, ovary or eye, is a collection of tissues with a specific job. There are several organ systems in the body that are organized in a similar way. For example, the organs in the digestive and respiratory systems all have passageways that are lined by epithelial tissue and are surrounded by layers of smooth muscle. Organ systems work together to perform specific jobs. The organs in our digestive system help to absorb nutrients from our food and get rid of waste. The organs in our respiratory system work together to allow us to breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. Some organs have more than one job.
The main organ systems are:
nervous system– the brain, spinal cord and nerves
respiratory system– the nose, mouth, windpipe (trachea), bronchi and lungs
cardiovascular system– the heart, blood vessels and blood
digestive (gastrointestinal) system– includes mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines (bowels), liver, pancreas and gallbladder
lymphatic system– includes lymph vessels, lymph fluid, lymph nodes, tonsils, thymus and spleen
endocrine system– includes the adrenal glands, ovaries, testicles (testes), pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands and part of the pancreas
urinary system– the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra
male reproductive system– includes the penis, testicles, seminal vesicles and prostate
female reproductive system– includes the vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries and breasts
muscoskeletal system– bones, cartilage, muscles and tendons
integumentary system– skin, hair, nails and sweat glands
Your trusted source for accurate cancer information
With support from readers like you, we can continue to provide the highest quality cancer information for over 100 types of cancer.
We’re here to ensure easy access to accurate cancer information for you and the millions of people who visit this website every year. But we can’t do it alone.
Every donation helps fund reliable cancer information, compassionate support services and the most promising research. Please give today because every contribution counts. Thank you.
